From June 20 to 22, the Chinese Academy of EngineeringŌĆÖs Science and Technology SymposiumŌĆöPolymer Recycling and Sustainable Development and the 8th Polymer Recycling and Upcycling SymposiumŌĆöwas successfully held in Chengdu.
At the thematic session on “Bio-based and Biodegradable Polymer Materials,” Mr. Chen Rui, Deputy General Manager of Shenzhen eSUN Industrial Co., Ltd., delivered a technical report titled High-Value Applications and Recycling of Bio-Based Biodegradable Polyester Materials.

Biodegradable polyester materials are derived from a wide range of sources, offer strong design flexibility, are easy to process, and exhibit excellent mechanical properties and biocompatibility. These advantages make them widely applicable in the medical, food packaging, agricultural, and industrial fields.
As one of the earliest companies in China to engage in biopolymer development, Shenzhen Esun Industrial Co., Ltd. (brand name ŌĆ£eSUNŌĆØ) has long focused on the R&D and application of biodegradable polyester materials. Through continuous innovation in the synthesis and modification of biopolymers, the company is expanding into high-value biomedical applications, supporting the green transformation and sustainable development of the industry.
I. Biomedical Applications of Biodegradable Polyester Materials
Biodegradable polyester materials can be widely applied in the biomedical field, including cardiovascular interventional treatment, neurosurgery, orthopedics/sports medicine, plastic and maxillofacial surgery, ENT, medical aesthetics, general surgery, oncology, and regenerative medicine.
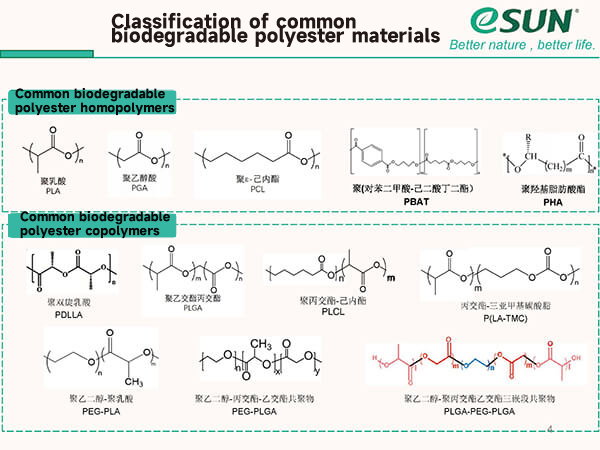
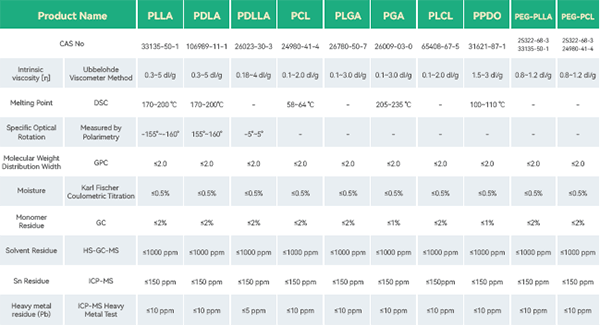
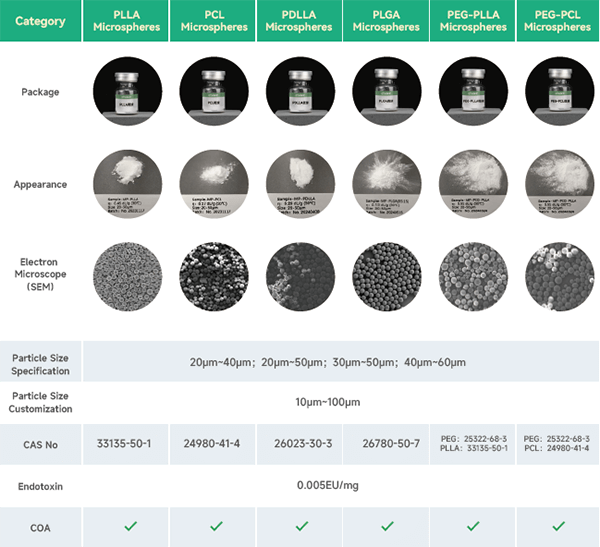
eSUNMED specializes in medical monomers, biodegradable polyesters (including PLA, PCL, PGA, and their copolymers), polyester microspheres, polyester-based composite materials, FDM 3D printing filaments, and SLS 3D printing powders. The company also provides high-precision molding and processing services, meeting the requirements for the development and application of various implant-grade absorbable medical devices.
II. Recycling and Reuse of Biodegradable Polyester Materials
To some extent, biodegradation also implies a form of waste. eSUN addresses this by achieving circular recycling of polylactic acid (PLA) materials through both physical and chemical recycling methods.
1. Physical Recycling and Reuse
Recycled PLA materials can be reused in fiber and 3D printing applications through physical recycling processes, reducing resource waste and enhancing economic efficiency.
2. Chemical Recycling and Reuse of PLA
Since establishing its PLA industry development strategy in 2003, eSUN has spent over two decades building a green closed-loop technology system encompassing material synthesis, modification, application, by-product digestion, and polymer chemical recycling. This has culminated in a uniquely structured X-type production technology framework. Within this system, lactide intermediates can be produced either from lactic acid or recycled PLA. These intermediates can then be used to manufacture PLA and PLA polyols, or for the co-production of lactate esters.
eSUNŌĆÖs project ŌĆ£Technology for Producing Lactide and Its Applications Using Lactic Acid and Recycled PLA as Raw MaterialsŌĆØ was appraised by the China National Light Industry Council as: ŌĆ£The overall technology reaches an internationally advanced level, with leading global status in the upcycling of PLA into lactate esters.ŌĆØ Currently, eSUNŌĆÖs chemical recycling-based lactide production line with an annual capacity of 5,000 tons has been industrially validated.
As sustainable consumption becomes a global consensus, the development of bio-based biodegradable polyester materials is a crucial pathway to addressing plastic pollution, promoting low-carbon transition, and supporting the high-quality development of a green economy. This endeavor holds significant ecological, economic, and strategic value.